Installation¶
Welcome to the NEBULA platform installation guide. This document explains how to obtain, install, run, and troubleshoot NEBULA.
Prerequisites¶
For the best experience, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Linux (Ubuntu 20.04 LTS recommended) or macOS (10.15 Catalina or later). Currently, we do not maintain an up-to-date version for Windows.
- Minimum 8 GB RAM (+32 GB recommended for virtualized devices).
- Minimum 20 GB disk space for Docker images and containers. Additional space is required for datasets, models, and results.
- Docker Engine 24.0.4 or higher (24.0.7 recommended, https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/)
- Docker Compose 2.19.0 or higher (2.19.1 recommended, https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/)
Obtaining NEBULA¶
You can obtain the source code from https://github.com/CyberDataLab/nebula
Or clone the repository using git:
user@host:~$ git clone https://github.com/CyberDataLab/nebula.gitNow, you can move to the source directory:
user@host:~$ cd nebulaInstalling NEBULA¶
Install required dependencies and set up Docker containers by running:
user@host:~$ make installNext, activate the virtual environment:
user@host:~$ source .venv/bin/activateIf you forget this command, you can type:
user@host:~$ make shellYour shell prompt should look similar to:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$Using NVIDIA GPU on Nodes (Optional)¶
For nodes equipped with NVIDIA GPUs, ensure the following prerequisites:
- NVIDIA Driver: Version 525.60.13 or later.
- CUDA: Version 12.1 is required. After installation, verify with
nvidia-smi. - NVIDIA Container Toolkit: Install to enable GPU access within Docker containers.
Follow these guides for proper installation:
Note: Ensure that the CUDA toolkit version is compatible with your driver and, if needed, update the Docker runtime to support GPU integration.
Running NEBULA¶
Once the installation is finished, you can check if NEBULA is installed properly using:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$ python app/main.py --versionTo run NEBULA, you can use the following command line:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$ python app/main.pyNote: The first run may build the nebula-frontend Docker image, which can take a few minutes.
Display available parameters:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$ python app/main.py --helpBy default, the frontend is available at http://127.0.0.1:6060. If the 6060 port is unavailable, a random port will be assigned automatically and prompted in the console.
Also, you can define the specific port using the following command line:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$ python app/main.py --webport [PORT]and the default port of the statistics endpoint:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$ python app/main.py --statsport [PORT]NEBULA Frontend Credentials¶
You can log in with the default credentials:
- User: admin
- Password: admin
If these do not work, please contact Enrique Tomás Martínez Beltrán at [email protected].
Stopping NEBULA¶
To stop NEBULA, you can use the following command line:
(nebula-dfl) user@host:~$ python app/main.py --stopBe careful! This command will stop all the containers related to NEBULA: Frontend, Controller, and Nodes.
Troubleshooting¶
If frontend is not working, check the logs in app/logs/frontend.log
If any of the following errors appear, take a look at the docker logs of the nebula-frontend container:
user@host:~$ docker logs user_nebula-frontendNetwork nebula_X Error failed to create network nebula_X: Error response from daemon: Pool overlaps with other one on this address space
Solution: Delete the docker network nebula_X
user@host:~$ docker network rm nebula_XError: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
Solution: Start the docker daemon
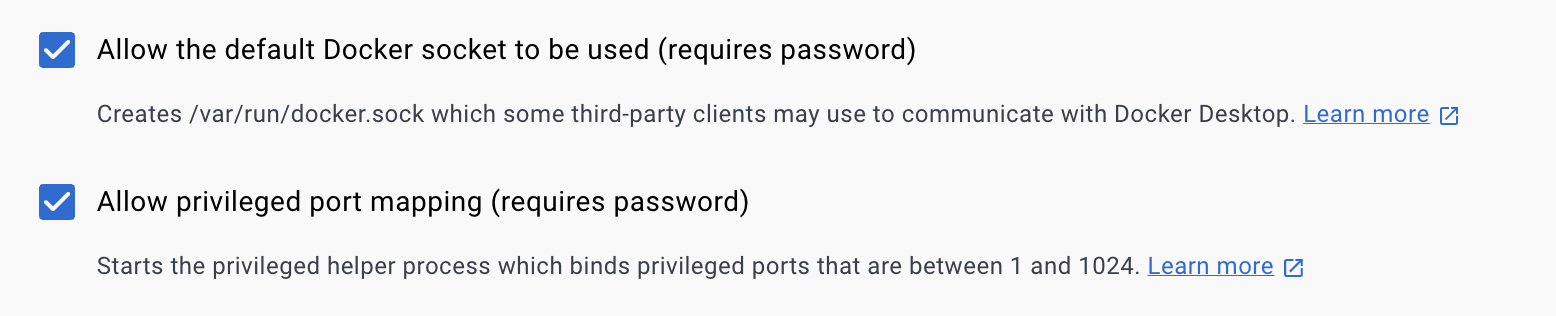
user@host:~$ sudo dockerdXSolution: Enable the following option in Docker Desktop
Settings -> Advanced -> Allow the default Docker socket to be used
Error: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at tcp://X.X.X.X:2375. Is the docker daemon running?
Solution: Start the docker daemon
user@host:~$ sudo dockerd -H tcp://X.X.X.X:2375If frontend is not working, restart docker daemon
user@host:~$ sudo systemctl restart dockerError: Too many open files
Solution: Increase the number of open files
ulimit -n 65536
Also, you can add the following lines to the file /etc/security/limits.conf
- soft nofile 65536
- hard nofile 65536